Nowadays, email is still a key part of business communication. But as we use more mobile devices and touchscreens, the chance of making fat-finger error mistakes from pressing the wrong keys or buttons has increased a lot.
These small errors can lead to big problems, greatly if they accidentally share sensitive information. This article looks at the risks of fat-finger mistakes in email and offers ways to avoid them.
What is Fat Finger Error?
A fat finger error is a term used to describe mistakes that occur when someone accidentally presses the wrong button or key, on a small or crowded keyboard or touchscreen. These errors are common when typing on mobile devices, where the small size of the screen and the keys make it easy to hit the wrong letter or number.
For example, you intend to type an email address but accidentally send it to the wrong person because you tapped on the wrong name in your contacts list.
According to the 2023 Egress Email Risk Report, 54% of organizations experienced reputational damage due to data breaches, and 48% faced employee-related issues. While these breaches aren’t just caused by fat finger errors, misdirected emails from human mistakes are significant contributors to these incidents.
What are the Common Causes of Fat Finger Errors?
There are multiple causes of fat-finger errors, with some of the most common ones detailed below.
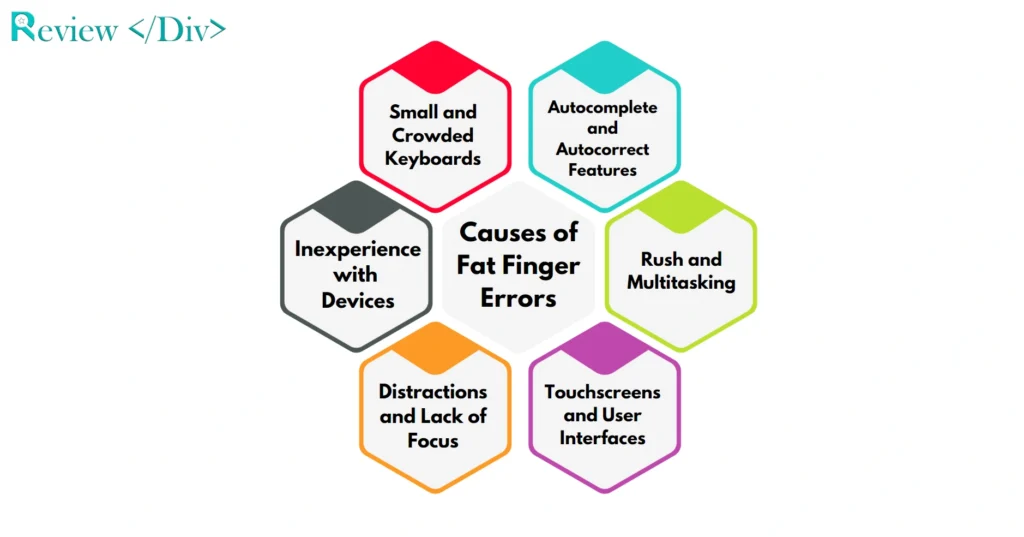
1. Small and Crowded Keyboards
One of the primary causes of fat finger errors is the use of small and crowded keyboards, especially on mobile devices. The limited space makes it easy to press the wrong key or button unintentionally.
2. Autocomplete and Autocorrect Features
Autocomplete and autocorrect features, designed to improve typing efficiency, can sometimes contribute to fat finger errors. For example, an email client’s autocomplete function suggests the wrong recipient, leading to a misdirected email.
3. Rush and Multitasking
People multitask and try to complete tasks quickly. This sense of urgency can lead to mistakes, as users may not take the time to carefully review their inputs. Rushing through typing or clicking can easily result in pressing the wrong keys or selecting incorrect options.
4. Touchscreens and User Interfaces
Touchscreens are another common source of fat finger errors. The touch-sensitive nature of these screens can lead to unintended taps or swipes. Also, user interfaces that are not well-designed or are too complex can contribute to mistakes.
5. Distractions and Lack of Focus
Distractions and lack of focus can also lead to fat finger errors. When users are not fully paying attention to what they are doing they are more likely to make accidental inputs. Maintaining concentration and minimizing distractions are important to reducing these errors.
6. Inexperience with Devices
Inexperience or unfamiliarity with a particular device or software can increase the likelihood of fat finger errors. Users who are not familiar with the layout of a new keyboard, touchscreen, or application interface may make more mistakes as they learn to navigate the new system.
Fat Finger Misdirected Email Example
Here is an example of a Fat Finger Misdirected Email.
Subject: Urgent Financial Report
Dear Team,
I hope this email finds you well. Attached, please find the financial report for Q2. It contains sensitive information related to our upcoming merger. Kindly review it and provide your feedback by the end of the day.
Recipient: John Doe Intended Recipient: Jane Smith
Unfortunately, due to a fat-finger error, I accidentally sent this email to John Doe instead of Jane Smith. I apologize for any inconvenience caused. Please ensure that this information remains confidential.
Thank you for your understanding.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
In this scenario, the sender intended to share the financial report with Jane Smith but mistakenly selected John Doe from the autocomplete list. Such errors can have serious results, mainly when dealing with sensitive data.
Risks and Consequences of Fat Finger Misdirected Emails
Misdirected emails can lead to data breaches, exposing sensitive information to unauthorized recipients. This can result in financial losses, legal consequences, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Accidentally sending confidential information to the wrong person can compromise business operations and strategic plans. It can also lead to competitive disadvantages if information is disclosed to competitors.
Organizations are subject to various data protection regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. Misdirected emails that result in data breaches can lead to significant fines and legal actions, as well as mandatory reporting and remediation efforts.
What are the Common Fat Finger Errors in Email?
There are many common fat-finger errors in email including sending messages to the wrong recipient due to misclicks or typing errors or more. Here are the Common Fat Finger Errors in detail.
1. Selecting the Wrong Recipient
Autocomplete features, designed to improve efficiency, can sometimes lead to selecting the wrong recipient from a contact list. This is especially problematic when similar names appear in the suggestions, resulting in misdirected emails.
2. Choosing the Wrong Attachment
Attaching the wrong file to an email is a common fat-finger mistake. This can happen when files are stored in a similar location or have similar names, making it easy to click on the incorrect one.
3. Forgetting the “Bcc” Field
Failing to use the “Bcc” (blind carbon copy) field when sending emails to multiple recipients can inadvertently expose email addresses to all recipients. This not only breaches privacy but can also lead to data protection issues.
4. Inappropriate “Reply All”
Using “Reply All” instead of “Reply” can unintentionally share sensitive information with a larger group than intended. This is a particularly common fat-finger error in corporate environments where group emails are frequent.
How to prevent Fat Finger Errors?
To prevent Fat Finger Errors or sending Misdirected emails, here are some steps that can help you.
Encryption at Message Level: Implementing message-level encryption can help reduce the effect of misdirected emails. Encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can access the email content, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
User Training: Educating employees about common fat-finger errors and best practices for avoiding them is important. Regular training sessions can help raise awareness and reinforce the importance of careful email handling.
Double-Check Recipients: Encouraging employees to take a moment to verify the recipients before sending an email can significantly reduce the risk of misdirected messages. A simple double-check can prevent many common mistakes.
Use “Bcc” Wisely: When sending emails to multiple recipients, using the “Bcc” field can protect the privacy of recipients and prevent accidental exposure of email addresses. This is especially important for large distribution lists.
Hover Over Links: On desktop devices, hovering over links before clicking can help identify phishing attempts and malicious websites. Encouraging this practice can enhance security awareness and prevent accidental clicks on harmful links.
Review Before Sending: A thorough review of the email content, attachments, and recipients before hitting the send button is a simple yet effective strategy to prevent fat-finger errors. This habit can catch mistakes before they become problems.
FAQs
A fat-finger mistake occurs when someone accidentally presses the wrong key or button, often due to the small size of keyboards or touchscreens. These errors can lead to unintended actions, such as sending emails to the wrong recipient or making incorrect data entries.
Fat-finger errors are quite common, especially with the increased use of mobile devices and touchscreens, where small keys and screens make it easy to press the wrong buttons.
Yes, they can be minimized through careful review of email recipients, user training, the use of email encryption, and implementing verification steps before sending sensitive information.
Immediately contact the unintended recipient, request that they delete the email without reading it, and inform your IT or compliance department to assess the situation and take necessary actions.
Yes, there are email security solutions and plugins that can alert users to potential errors, verify recipients, and recall emails if they are sent to the wrong person.
Some email services, like Microsoft Outlook, offer a recall feature that allows you to attempt to retract an email sent to the wrong recipient. However, success depends on the recipient’s email settings and whether they have already opened the email.
Laura Kemmis is a passionate trendsetter and reviewer, dedicated to researching the latest scams and frauds while sharing her insights with the world. She provides valuable information to keep her audience aware and informed about the latest scams. Additionally, Laura discovers and analyzes trends in fashion, technology, and lifestyle, offering a fresh and honest perspective in her reviews.