Cybersecurity threats have become more advanced with spear phishing occurring as one of the most dangerous. Unlike traditional phishing, which targets a broad audience with generic messages.
spear phishing is a highly targeted cyberattack. It seeks to deceive individuals or organizations into revealing sensitive information. This post explores the nature of spear phishing, how it works, and why preventing email-based attacks remains challenging.
What Is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing attacks involve detailed research and personalization. Instead of sending out generic emails to a large group, cybercriminals focus on a specific individual or organization.
They gather as much information as possible about their target, which they then use to create effective emails that appear to come from trusted sources like colleagues, business partners, or friends.

The main goal of spear phishing is often to steal sensitive information, such as login certificates or financial data, or to install malware on the victim’s device.
The risk of spear phishing lies in its effectiveness, and the high level of realization makes it difficult for even alert individuals to recognize the threat.
How Does Spear Phishing Work?
Spear phishing begins with attackers gathering detailed information about their target. They collect personal details like names, job titles, email addresses, and specific interests by using social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter.
Attackers also research company websites, news articles, and press releases. Sometimes, they engage in fake conversations, a tactic known as “pretexting,” to extract more information.
With this information, attackers craft an email that seems to come from a trusted source, like a colleague, friend, or familiar business. The message mimics the writing style, tone, and urgency associated with the supposed sender.
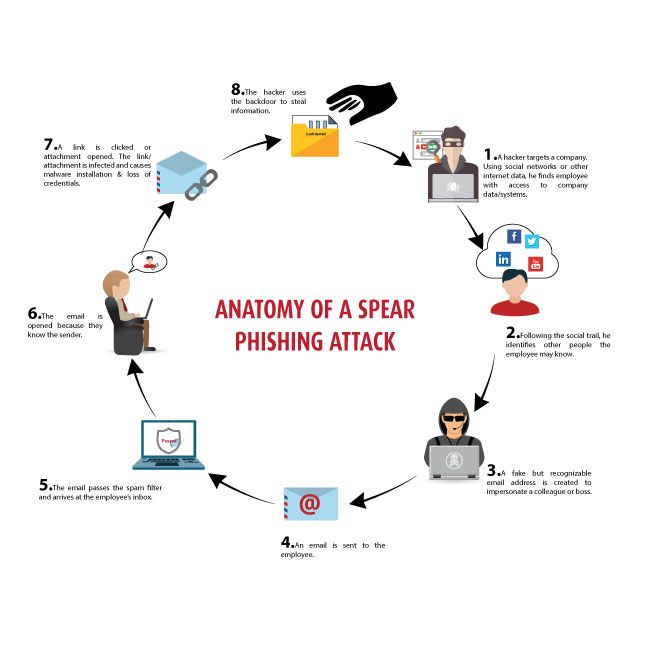
They imitate a CEO or high-ranking executive, referencing recent company events or ongoing projects to make the email appear legitimate. The email includes an opposing link or attachment. it is created to install malware on the target’s device or direct them to a fake website that steals sensitive information.
Once the target receives the email and clicks on the link or downloads the attachment, the spear phishing attack is set in action. The malware may silently install itself on the victim’s computer and provide the attacker access to the network.
With access to the target’s system or information, the attacker can exploit their success, stealing financial data, or confidential business information. they also, use the compromised account to launch further attacks within the organization deepening their infiltration.
The consequences of a successful spear phishing attack can be extreme financial loss, reputational damage, and a significant breach of trust.
Why Email Attacks Are Difficult To Stop?
Many things can make email attacks difficult to stop, here are some major things that can make this difficult and you should also know these points for your awareness.
1. The Trojan Horse
Attackers don’t rely on random chances they research their targets and craft emails that feel genuine and trustworthy. This level of realization can trick even the most cautious individuals because it doesn’t trigger the usual warning signs associated with generic phishing emails.
2. Manipulating Human Behavior
These attacks go beyond technology, they play on human emotions and psychology. Attackers create a sense of urgency or fear, pressuring victims to act quickly without thinking. This manipulation directs people even those who are usually careful to make mistakes like clicking on malicious links or sharing information.
3. Slipping Through the Cracks
Traditional security tools like spam filters and antivirus software are ineffective against spear phishing. These attacks are customized and carefully crafted to avoid detection. Since the emails appear to come from trusted sources. They can easily bypass standard defenses and reach the planned victim.
4. Staying One Step Ahead
Cybercriminals constantly update their methods to outsmart security measures. As soon as new defenses are put in place, attackers find new ways to get around them. This ongoing cat-and-mouse game makes it difficult for security systems to keep pace with the ever-evolving tactics of spear phishing.
5. The Weakest Link
People make mistakes mainly when they are tired, distracted, or unaware of the latest threats. Spear phishing exploits this exposure by targeting individuals, who are not always on their guard. It’s impossible to guarantee that everyone will always make the right decision.
How To Prevent Spear Phishing Attacks?
Preventing spear phishing attacks requires forceful measures that can significantly reduce the risks. Here are some key steps organizations can take.
Train Employees Regularly: Conduct training sessions to help employees recognize phishing attempts. By educating your team on the tactics used in spear phishing, you authorize them to identify suspicious emails and respond properly.
Implement Strong Security Protocols: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. Even if attackers obtain login credentials, MFA makes it harder for them to access accounts without a second verification step.
Use Advanced Email Filtering: Deploy advanced email filtering solutions to detect and block spear phishing attempts before they reach your inbox. These filters hold machine learning and other technologies to spot subtle signs of phishing.
Develop a Robust Incident Response Plan: Establish clear protocols for responding to suspected phishing attempts. An incident response plan allows your organization to react swiftly and minimize damage if an attack occurs.
Keep Systems and Software Updated: Regularly update your software and systems to reduce exposures that attackers could exploit. Keeping everything up to date supports your defenses against spear phishing attempts and other cyber threats.
FAQ’s
A real example is when an attacker poses as a trusted colleague and sends a personalized email asking for sensitive information or urging you to click a malicious link.
Spear phishing targets specific individuals, while whaling phishing specifically aims at high-profile executives or important figures within an organization.
Check for unusual requests, double-check the sender’s email address, and be cautious of urgent or unexpected messages.
Anyone can be targeted, but attackers often focus on employees with access to valuable information or financial resources.
Phishing attacks succeed because many users lack security awareness and can be easily fooled by personalized, convincing messages.
Jason Thomas is a Computer Science student specializing in AI & ML, dedicated to safeguarding individuals from online threats. Passionate about exposing internet scams, Jason spends his free time identifying and reviewing various fraudulent activities and unethical materials. With a unique blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application, he is a valuable contributor to the fight against online fraud. His commitment to technology and programming fuels his mission to protect people from scams and enhance internet safety for everyone.